Intrinsic parameters
http://ksimek.github.io/2013/08/13/intrinsic/
Extrinsics
http://ksimek.github.io/2012/08/22/extrinsic/
Thursday, August 2, 2018
Thursday, June 28, 2018
Ubuntu mount local network shared folder
Server end
- Install Samba
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install samba
- Set a password for your user in Samba
sudo smbpasswd -a <user_name>
Note: Samba uses a separate set of passwords than the standard Linux system accounts (stored in /etc/samba/smbpasswd), so you'll need to create a Samba password for yourself. This tutorial implies that you will use your own user and it does not cover situations involving other users passwords, groups, etc...
Tip1: Use the password for your own user to facilitate.
Tip2: Remember that your user must have permission to write and edit the folder you want to share. Eg.: sudo chown <user_name> /var/opt/blah/blahblah sudo chown :<user_name> /var/opt/blah/blahblah
Tip3: If you're using another user than your own, it needs to exist in your system beforehand, you can create it without a shell access using the following command : sudo useradd USERNAME --shell /bin/false You can also hide the user on the login screen by adjusting lightdm's configuration, in /etc/lightdm/users.conf add the newly created user to the line : hidden-users=
- Create a directory to be shared
mkdir /home/<user_name>/<folder_name>
- Make a safe backup copy of the original smb.conf file to your home folder, in case you make an error
sudo cp /etc/samba/smb.conf ~
- Edit the file "/etc/samba/smb.conf"
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
Once "smb.conf" has loaded, add this to the very end of the file: [<folder_name>] path = /home/<user_name>/<folder_name> valid users = <user_name> read only = no
Tip: There Should be in the spaces between the lines, and note que also there should be a single space both before and after each of the equal signs.
- Restart the samba:
sudo service smbd restart
- Once Samba has restarted, use this command to check your smb.conf for any syntax errors
testparmT
Client end
- access your network share
sudo apt-get install smbclient # List all shares: smbclient -L //<HOST_IP_OR_NAME>/<folder_name> -U <user> # connect: smbclient //<HOST_IP_OR_NAME>/<folder_name> -U <user>To access your network share use your username (<user_name>) and password through the path "smb://<HOST_IP_OR_NAME>/<folder_name>/" (Linux users) or "\\<HOST_IP_OR_NAME>\<folder_name>\" (Windows users). Note that "<folder_name>" value is passed in "[<folder_name>]", in other words, the share name you entered in "/etc/samba/smb.conf". Note: The default user group of samba is "WORKGROUP".
2. mount
sudo mount -o username=<> //172.29.32.184/sharename /media/Data/
for windows
sudo mount -t cifs -o username=<> //172.29.32.184/sharename /media/Data/
- Note- If you receive the error:
wrong fs type, bad option, bad superblock on...make sure you have cifs-utils installed, it may not be installed on your distro by default.sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
Sunday, June 24, 2018
BUG: tensorflow tf.scatter_nd will accumulate (or undermined) values when indices have duaplicates
Problem:
WARNING: The order in which updates are applied is nondeterministic, so the output will be nondeterministic if
Solution:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/8102
2. Solution
Use a count auxilliary tensor.
WARNING: The order in which updates are applied is nondeterministic, so the output will be nondeterministic if
indicescontains duplicates.Solution:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/8102
If you are in the unpooling business:
@teramototoya what I did as a hack: with https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/unique_with_counts i counted the multiplication in the indices and i divided the tensor which was holding the values (aka tensor named 'updates' in the first comment) with this counter
so when add() comes it will undo what the division made
so when add() comes it will undo what the division made
you can check this simple script: https://github.com/csnemes2/conv-net-viz/blob/master/ut_unpool.py
If not, so your problem is general, then you have to somehow flatten your indices, and then tf.unique, see this post:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44117430/how-to-use-tf-scatter-nd-without-accumulation
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44117430/how-to-use-tf-scatter-nd-without-accumulation
Use a count auxilliary tensor.
cntOnes = tf.ones_like(dmVis, tf.float32)
vals = tf.stack([dmVis, mlVis, cntOnes], axis=1)
scatter_shape = tf.constant([bs, h*upsample, w*upsample, 3])
dmc = tf.scatter_nd(locVis, vals, scatter_shape)
dm, ml, cnt = tf.unstack(dmc, axis=-1)
cnt = cnt + epsilon
dm = dm / cnt
Monday, June 4, 2018
Remote VSCode Setup
Remote VSCode Setup
So this is where the Remote VSCode comes in. Remote VSCode is a Visual Studio Code extension that is available in all platforms supported by VSCode (yes, including both Windows and macOS), that implements the Textmate’s ‘rmate’ feature. This extension allows you to edit your files from your virtual machine a lot easier.
To use the extension, do the following:
- Launch Visual Studio Code, or install it here if you don’t have it yet
- Go to the ‘Extensions’ page and search for ‘Remote VSCode’
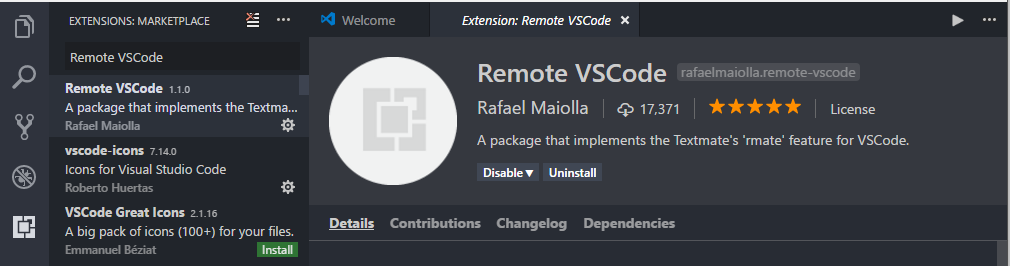
3. Install the extension and re-launch Visual Studio Code
4. In your Linux Virtual Machine, execute the following command in your terminal to install rmate
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/rmate https://raw.github.com/aurora/rmate/master/rmate
$ sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/rmate
5. Go back to your Visual Studio Code and open up the command palette (CTRL+P for Windows and CMD+P for Mac) then execute the
>Remote: Start Server command.
6. Once the server is ready, open up a new terminal and connect to your Linux Virtual Machine using the following command:
$ ssh -R 52698:localhost:52698 VIRTUAL_MACHINE_IP_ADDRESS
7. In your terminal, execute the
rmate command with the file that you want to open up in your Visual Studio Code in your local machine$ rmate demo.py
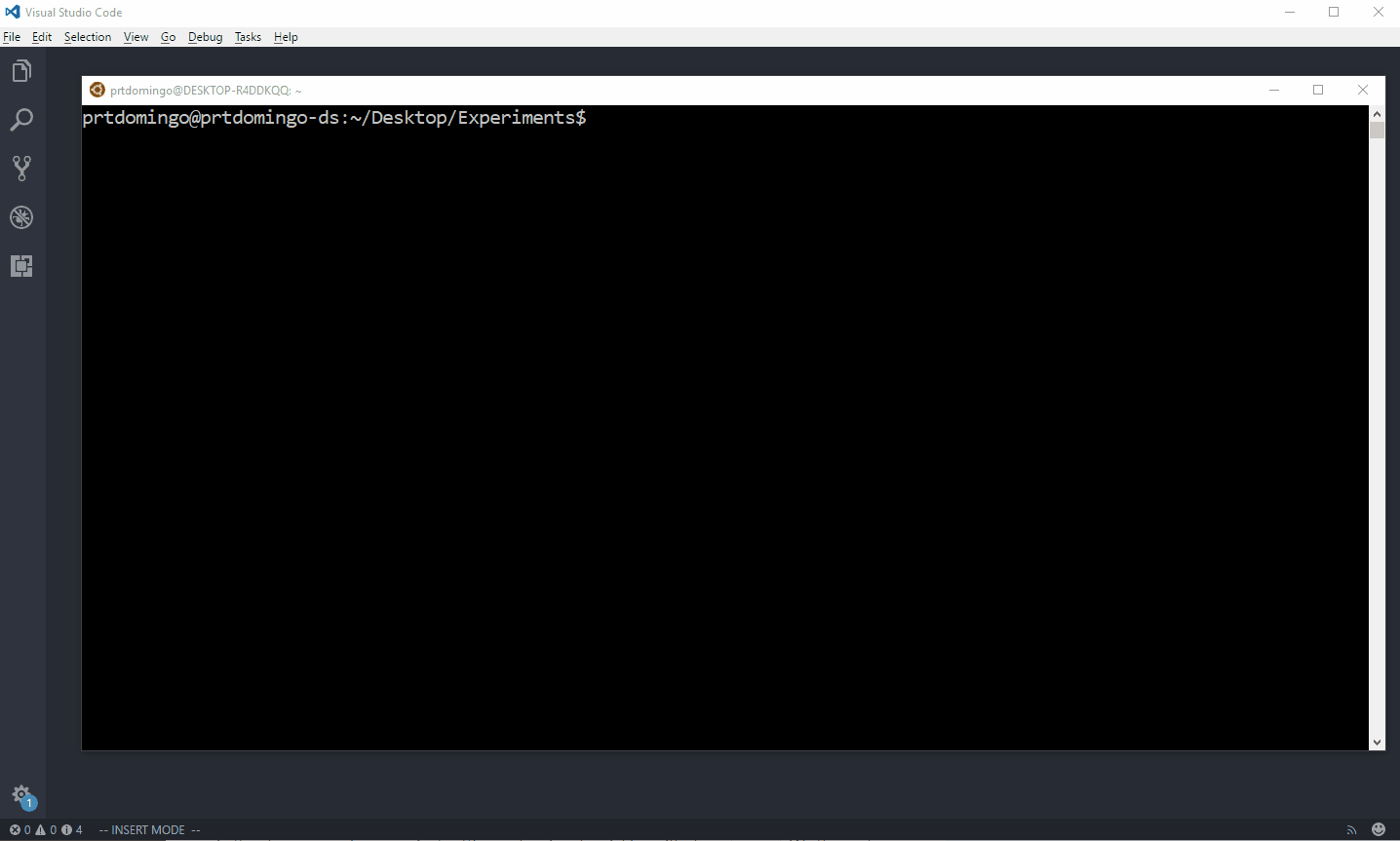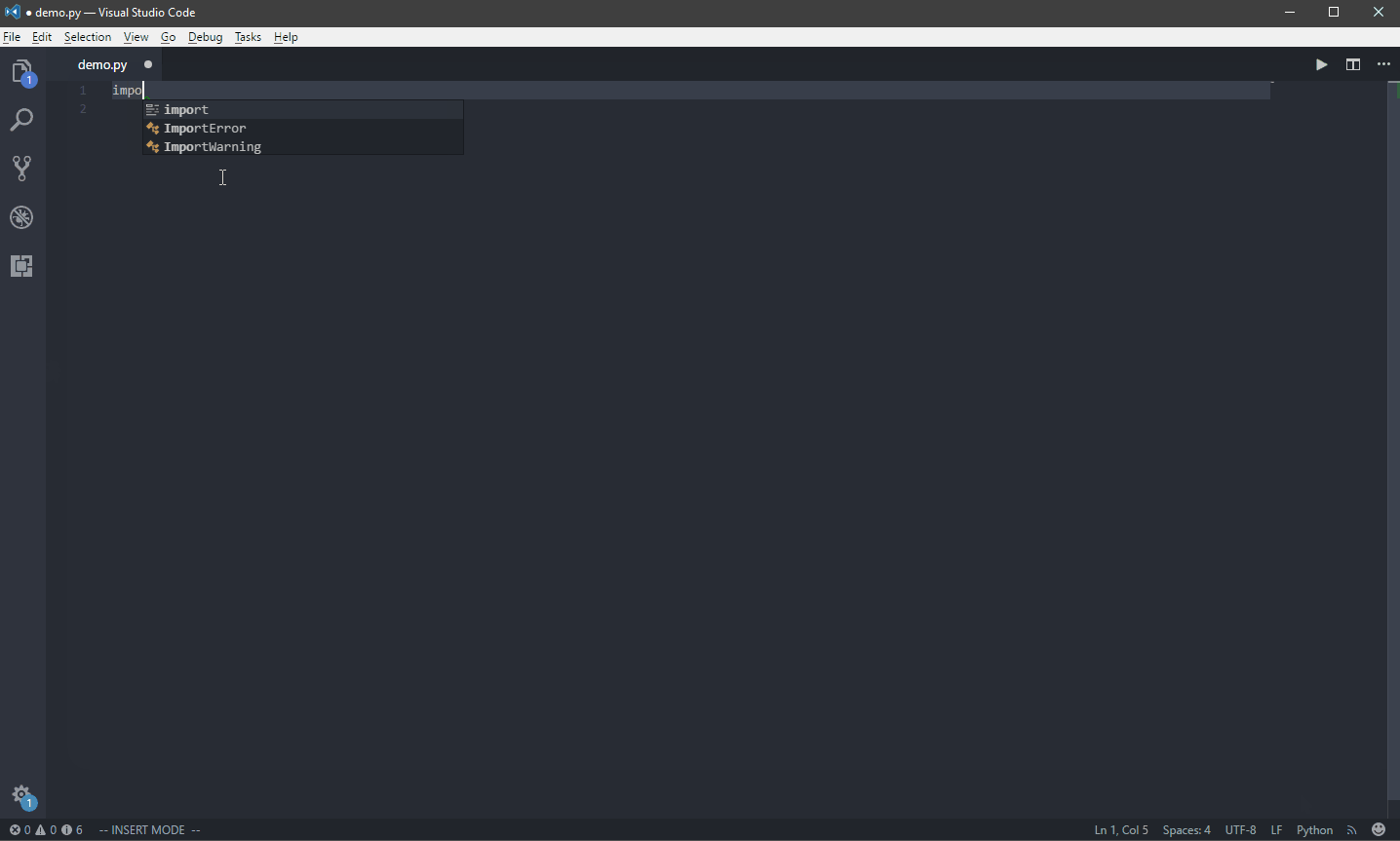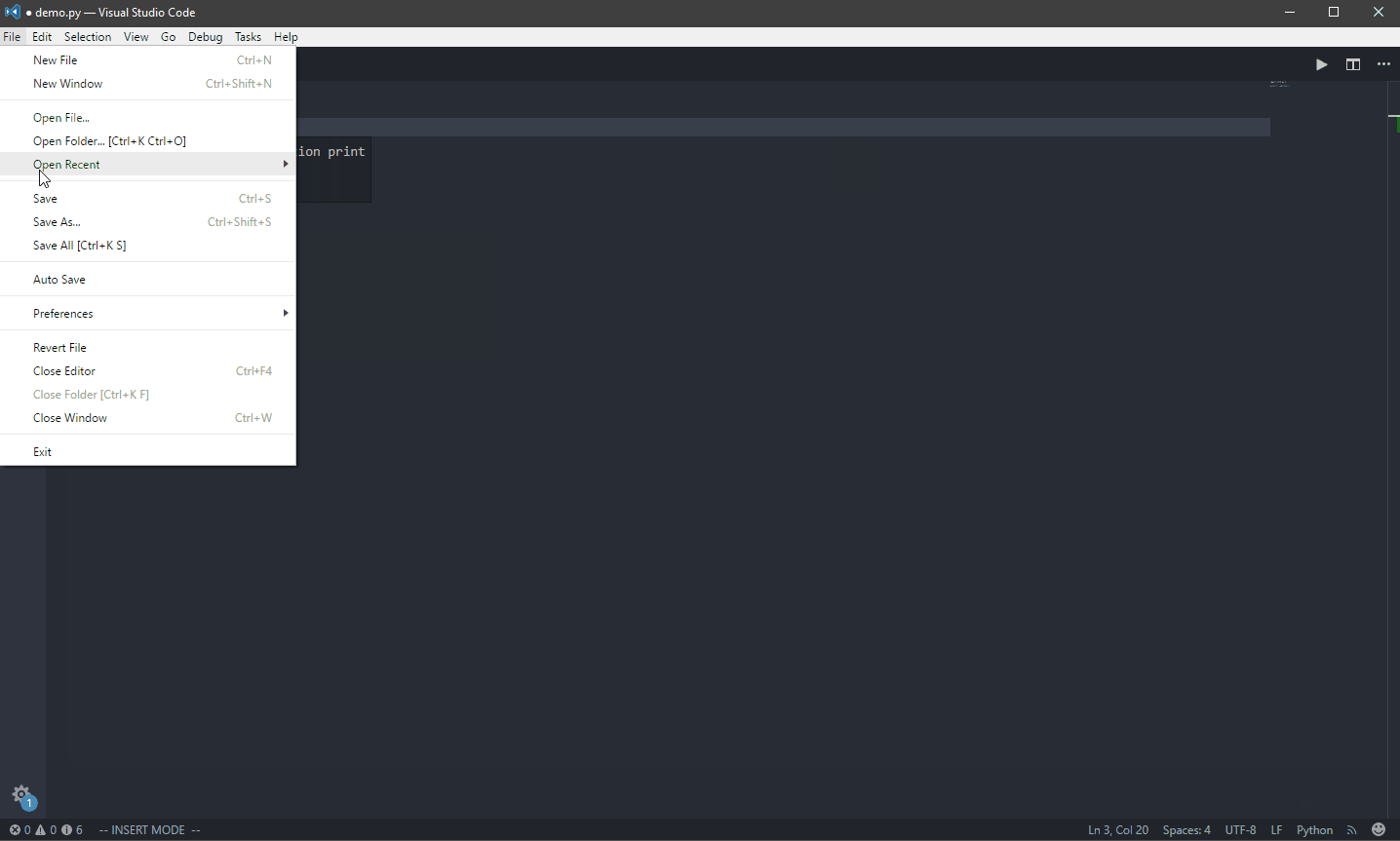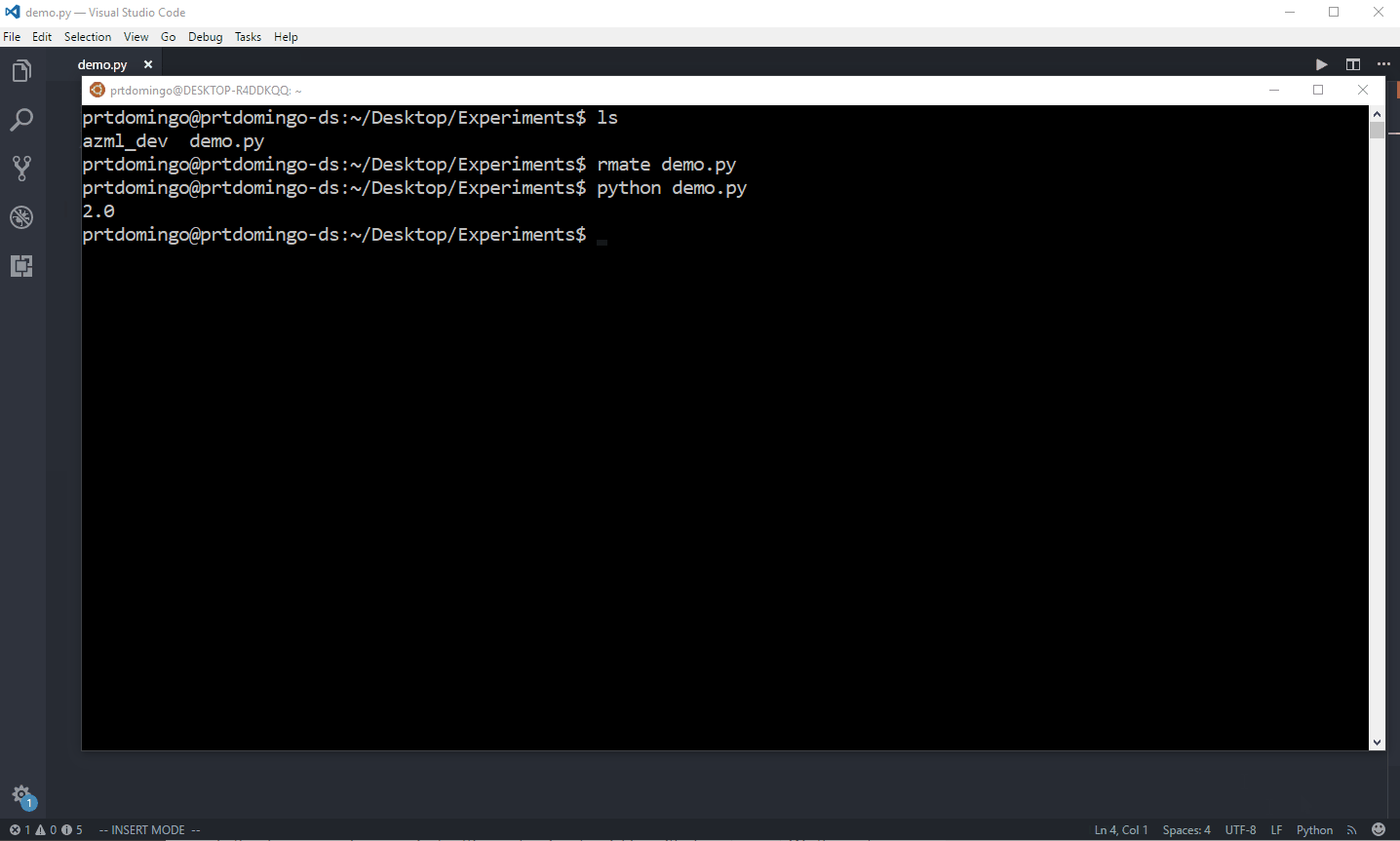
Just in case you’re also wondering where the
52698 port came from, it’s actually the default port that Remote VSCode is using. You can find and change that setting by simply going to your ‘User Preferences’ and search for ‘Remote VSCode configuration’.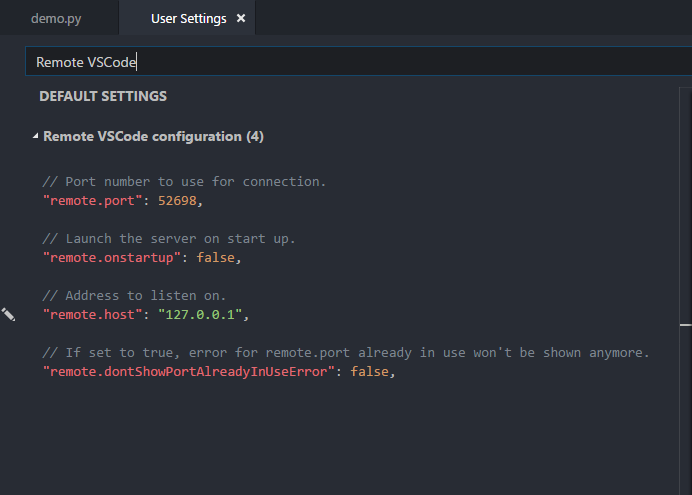
Monday, May 21, 2018
Motivation of 3D Scene Understanding
Some extract from papers, but may be minorly modified by me.
At the heart of the 3D inference problem is the question: What are the right primitives (representations) for inferring the 3D world from a 2D image? It is not clear what kind of 3D primitives can be directly detected in images and be used for subsequent 3D reasoning. There is a rich literature proposing a myriad of 3D primitives ranging from edges and surfaces to volumetric primitives such as generalized cylinders, geons and cuboids. While these 3D primitives make sense intuitively, they are often hard to detect because they are not discriminative in appearance. On the other hand, primitives based on appearance might be easy to detect but can be geometrically uninformative.
They propose geometric primitives which are visually-discriminative, or easily recognized in a scene, and geometrically-informative, or conveying information about the 3D world when recognized.
Data-Driven 3D Primitives for Single Image Understanding
How do you infer the 3D properties of the world from a 2D image? This question has intrigued researchers in psychology and computer vision for decades. Over the years, researchers have proposed many theories to explain how the brain can recover rich information about the 3D world from a single 2D projection. While there is agreement on many of the cues and constraints involved (e.g., texture gradient and planarity), recovering the 3D structure of the world from a single image is still an enormously difficult and unsolved problem.At the heart of the 3D inference problem is the question: What are the right primitives (representations) for inferring the 3D world from a 2D image? It is not clear what kind of 3D primitives can be directly detected in images and be used for subsequent 3D reasoning. There is a rich literature proposing a myriad of 3D primitives ranging from edges and surfaces to volumetric primitives such as generalized cylinders, geons and cuboids. While these 3D primitives make sense intuitively, they are often hard to detect because they are not discriminative in appearance. On the other hand, primitives based on appearance might be easy to detect but can be geometrically uninformative.
They propose geometric primitives which are visually-discriminative, or easily recognized in a scene, and geometrically-informative, or conveying information about the 3D world when recognized.
GeoNet: Geometric Neural Network for Joint Depth and Surface Normal Estimation
Albeit the great advancement in this filed (depth estimation), we notice that most previous methods deal with depth and normal estimation independently, which possibly make their prediction inconsistent without considering the close underlying geometry relationship. For example, as demonstrated in [], the predicted depth map cloud be distorted in planar regions. It is thus intriguing to ask what if one considers the fact that surface normal does not change much in planar regions. This thought motivates us to design new models, which are exactly based on above simple fact and yet potentially show a vital direction in this field, to exploit the inevitable geometric relationship between depth and surface normal for more accurate estimation.Wednesday, May 2, 2018
undefined reference to `xcb_dri3*'
Problem:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libGL.so: undefined reference to `xcb_dri3_buffers_from_pixmap
Analysis:
1. libGL.so not working
2. xcb not working
Solution:
1. check if libGL.so is working
ldd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libGL.so
if working: go to step 2
if not: install opengl
2. add -lxcb -lxcb-dri3
Note that we need to add all libs in the target makefile or qt pro file. Actually, I fix this with this solution.
3. sudo apt-get update
add -lxcb -lxcb-dri3
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libGL.so: undefined reference to `xcb_dri3_buffers_from_pixmap
Analysis:
1. libGL.so not working
2. xcb not working
Solution:
1. check if libGL.so is working
ldd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libGL.so
if working: go to step 2
if not: install opengl
2. add -lxcb -lxcb-dri3
Note that we need to add all libs in the target makefile or qt pro file. Actually, I fix this with this solution.
3. sudo apt-get update
add -lxcb -lxcb-dri3
Wednesday, March 28, 2018
modify tensorflow checkpoint path
The saved checkpoint stored the model absolute path. If you changed some path, you need to update the stored paths in checkpoint.
Two functions in
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.6/tensorflow/python/training/saver.py
1. get original state
get_checkpoint_state(checkpoint_dir, latest_filename=None)
2. Update the paths, similar in the got paths
def update_checkpoint_state(save_dir,model_checkpoint_path,
all_model_checkpoint_paths=None,
latest_filename=None)
# all_model_checkpoint_paths is a list
Two functions in
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.6/tensorflow/python/training/saver.py
1. get original state
get_checkpoint_state(checkpoint_dir, latest_filename=None)
2. Update the paths, similar in the got paths
def update_checkpoint_state(save_dir,model_checkpoint_path,
all_model_checkpoint_paths=None,
latest_filename=None)
# all_model_checkpoint_paths is a list
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)